Articles
Determination of macroelements in potable waters with cell-based inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry
With a wide range of concentrations of elements in potable waters, their accurate determination is difficult with ICP-MS. It is possible, using a cell-based instrument, to “tune” the signal sensitivity of particular elements and so keep all them within the dynamic range of the instrument.
Robust single method determination of major and trace elements in foodstuffs using the Thermo Scientific iCAP PRO X Duo inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer
A sponsored article demonstrating the ability of the Thermo Scientific™ iCAP™ PRO Series inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy instrument to determine trace elements and major components in foodstuffs to comply with regulations.
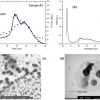
Characterisation of TiO2 pigments in commercial foundation creams: a synergic use of the ICP-AES, square wave voltammetry and sedimentation FFF techniques
TiO2 is widely used as a sunscreen UV filter and as a colouring agent in all types of cosmetic products. TiO2 has recently captured the attention of the scientific community since its safety assessment has been placed again under consideration. Inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), square wave voltammetry (SWV) and sedimentation field-flow fractionation (SdFFF) are described in this article to characterise and quantify the TiO2 particles inside six commercial foundation creams.
Using inductively-coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy to optimise the analysis of trace elements in gasoline
This article discusses how modern inductively-coupled plasma (ICP) technology surpasses the performance of traditionally used atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) techniques to ensure optimal fuel quality.
Laser ablation ICP atomic emission spectrometry: a new tool for imaging of pharmaceutical tablets
Imaging of organic and inorganic constituents of tablets represents a considerable challenge and no single spectroscopic approach can provide definitive characterisation of all components and/or satisfy key measurement criteria such as sensitivity, specificity, resolution and speed of analysis. Laser ablation in combination with ICP emission spectrometry represents a powerful new tool for imaging elemental distribution in pharmaceutical tablets.
The analysis of used lubrication oils by inductively coupled plasma spectrometry for predictive maintenance
Analysis of used lubrication oil for metals is commonplace in many industries. The metals analysed fall into three categories: wear metals, contaminants and additive elements. The concentration of these metals and elements can then be interpreted to schedule maintenance of engines and machinery such as construction machinery and aeroplanes. The cost of unscheduled maintenance can be high, not only in materials and parts, but also in lost profits due to downtime. Once the oil has been sampled, Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) analysis is a very useful tool for this application.
(Image courtesy Shell Motorsport)
The ICP-ToF mass spectrometer: an alternative for elemental analysis
Erwin Hoffmanna and Christian Lüdkeb
aGOS - Gesellschaft zur Förderung angewandter Optik, Optoelektronik, Quantenelektronik und Spektroskopie eV, Rudower Chaussee 29, 12489 Berlin, Germany. E-mail: [email protected]
bISAS–Institute for Analytical Sciences, Department Berlin, Albert-Einstein-Str. 9, 12489 Berlin, Germany